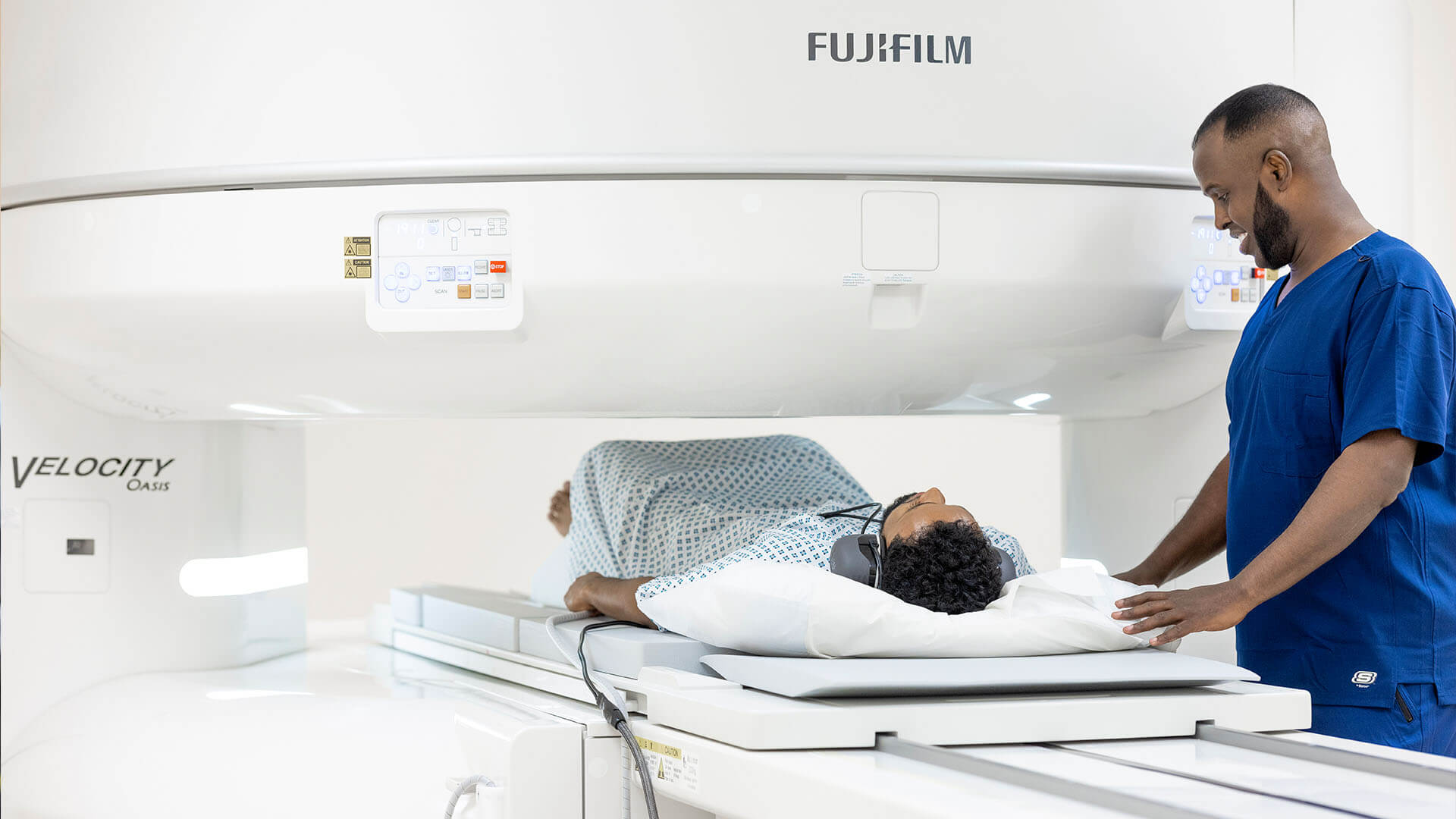
Better healthcare for those who don’t want to wait
VisitHealth combines immediacy, walk-in availability, mobility, the latest technology and the highest levels of service to deliver a new model for healthcare in the UK.
- Same day treatment
- Treatment at-home or in our central London clinic
- Latest innovative technology
Our consultants

VisitHealth has a wide range of experienced specialists that are available immediately to investigate anything that might be worrying you.
- Specialists covering all conditions
- Personalised approach to serving patients
- Supported by dedicated clinical teams

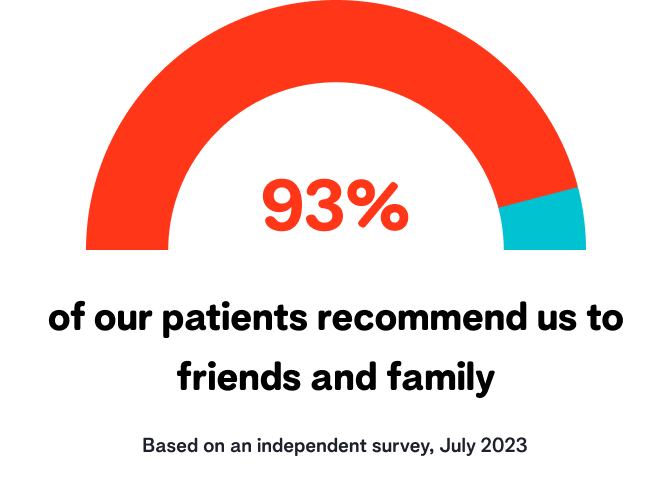
Our reviews




A word from our management
Prof. Ali Ghoz
Medical director

" What we’ve created is something no less than meaningful improvements to the people walking into our clinic: the Londoners, the new clients, and the hopeful patients flying in. Because our work removes undue waiting and travelling where possible, and because our specialists bring the care to your home in-person or through telehealth, the work we do here protects you from inconvenience and inattention and surrounds you with a team that can actually concentrate on your diagnosis and a refreshingly efficient turnaround.
If you visit VisitHealth, you’ll see what we mean. "